




[ENGN2211 Home]
Impedances
Ohm's law and impedances can be obtained from the s-domain
impedances of Table 2 in §3.2.4 on setting
 .
AC impedances are shown in Table 3, and
Ohm's law reads
.
AC impedances are shown in Table 3, and
Ohm's law reads
V = Z I
where
Z is the complex AC impedance,
and
V,
I are voltage and current phasors.
Table 3:
AC impedances.
| Resistor |
Z =R |
| Capacitor |
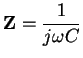 |
| Inductor |
 |
|
Ohm's law indicates the following phase relationships:
-
For resistors, current and voltage are in phase.
-
For capacitors, current leads voltage by
 .
.
-
For inductors, current lags voltage by
 .
.
This is illustrated in Figure 36.
Figure 36:
Phasor diagram indicating current-voltage phase relationships
for resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
 |
In general, impedances are complex numbers, and so we write
Z = R + j X
where
-
 is the resistive
component, and
is the resistive
component, and
-
 is the reactive
component, called the reactance.
is the reactive
component, called the reactance.
The admittance
is the reciprocal of impedance:
and we write
Y = G + j B
where
-
 is the conductance,
and
is the conductance,
and
-
 is the susceptance.
is the susceptance.





[ENGN2211 Home]
ANU Engineering - ENGN2211
![]() .
AC impedances are shown in Table 3, and
Ohm's law reads
.
AC impedances are shown in Table 3, and
Ohm's law reads
