 |
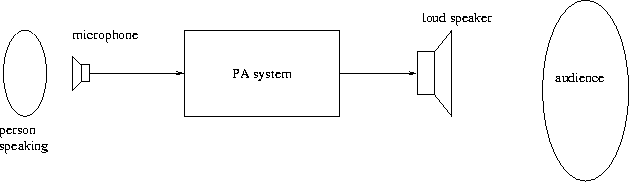
Think of a public address (PA) system, where a person speaks into a microphone and whose speech is amplified by the PA system and heard by the audience, Figure 1.
Ideally, distortion should be minimized, so the amplifier's outputs should be a magnified copy of the the speaker's voice.
The amount of amplification is determined by the gain, A. Mathematically,
this means
Example.
Suppose the gain A=10, and we
input a pure tone
![]() of amplitude 2V
and frequency
of amplitude 2V
and frequency
![]() rad/sec.
rad/sec.
Then the output is
![]() ,
with amplitude 2V and frequency
,
with amplitude 2V and frequency
![]() rad/sec,
Figure 3.
rad/sec,
Figure 3.
ANU Engineering - ENGN2211