AC analysis is a special case of dynamic analysis where we are interested in the time varying steady state waveforms (sinusoids); we ignore transient components. The important point is that when a linear circuit is driven by a sinusoidal AC source, its steady state response (i.e. currents and voltages) is also a sinusoid (of the same frequency, but of different magnitudes and phases). The method of phasors you have seen in first year is a short cut method for solving AC problems, although you could use differential equations or s-domain methods. Before we look at AC analysis proper let's do some bare hands calculations to help our understanding.
Consider the circuit of Figure 33.
Here,
![]() V, v(0-)=0 V,
R=1
V, v(0-)=0 V,
R=1 ![]() ,
and C=1 F. We are interested
in the capacitor voltage v(t).
,
and C=1 F. We are interested
in the capacitor voltage v(t).
The s-domain circuit is shown in
Figure 34.
Now
By KVL,
Exercise. Check all these calculations!
The term
![]() is indeed a sinusoid
of frequency 2 rad/sec, since by trigonometry
is indeed a sinusoid
of frequency 2 rad/sec, since by trigonometry
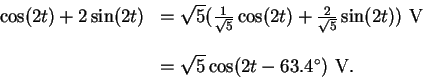
This type of calculation can get complicated,
and it is much simpler to use complex
currents and voltages.
Suppose we have
In equation (45) the term ej2t
is the complex sinusoid, while the complex number
ANU Engineering - ENGN2211