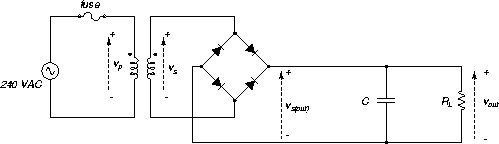
 |
You are to design a power supply based on the circuit of Figure 59 and meeting the specifications below. The power supply consists of a transformer supplied by the 240 V mains, a bridge rectifier, a capacitor smoothing filter and a load.
AC voltages.
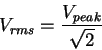
Fuse.
The fuse is included to protect the transformer from possible damage due to high or short circuit currents.
Transformer.
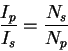
(The resistance of the transformer secondary is several ohms, obviating the need for a surge resistor here.)
Rectifier.
Filter.
Ripple voltage (bridge full-wave rectifier, peak-peak):
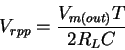
Ripple (peak-peak):
Load.
The load supplied by the power supply is modelled by a load resistor RL. The value of RL used in the design corresponds to full load current.
ANU Engineering - ENGN2211